SAP Technologies Comprehensive Reference
Executive Summary
This document covers the complete SAP technology ecosystem, from traditional on-premise systems to modern cloud-native solutions.
The SAP landscape has evolved significantly from its traditional R/3 roots to the modern S/4HANA and Business Technology Platform (BTP) era. Today's SAP professionals need to understand both legacy systems (which many companies still run) and next-generation cloud technologies.
SAP Ecosystem Overview
The SAP ecosystem consists of multiple layers working together to deliver comprehensive enterprise solutions.
- layer1 : Foundation layer where lies the technical infrastructure (BASIS, databases, operating systems)
- layer2 : Application layer (business modules like MM, SD, PM)
- layer3 : the top are the user interfaces and analytics tools.
Modern SAP architecture emphasizes cloud-first approaches, real-time analytics with HANA, and integrated business processes across the entire value chain. The shift toward S/4HANA represents SAP's vision of intelligent enterprises running on simplified, in-memory computing platforms.
Technology Categories
1. Operating Systems & Infrastructure
SAP OpenSUSE
- Acronym: SUSE Linux Enterprise Server (SLES) - SAP Edition
- Category: Operating System
- Purpose: Linux-based operating system specifically optimized for SAP applications. Provides the foundational platform for running SAP systems with enhanced performance, reliability, and support for SAP-specific requirements.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: N/A (continuously updated)
- Key Use Cases: Primary OS for SAP HANA deployments, S/4HANA systems, and other SAP applications requiring high availability and performance.
Linux Enterprise Server for SAP Operating System Applications | SAP HANA | SUSE
SUSE Rancher for SAP applications is the world’s most popular multi-cluster Kubernetes
Security
SAP on AWS
- Acronym: SAP on Amazon Web Services
- Category: Infrastructure
- Purpose: Cloud infrastructure solution that enables organizations to run SAP workloads on Amazon's cloud platform. Provides scalable, reliable infrastructure for SAP applications with various deployment options.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: N/A (evolving platform)
- Key Use Cases: Cloud migration of existing SAP systems, new SAP implementations, disaster recovery, and development/testing environments.
SAP Lens - AWS Well-Architected Framework Pillars:
- Operational excellence
- Security
- Reliability
- Performance efficiency
- Cost optimization
- Sustainability
AWS SDK for SAP ABAP AWS SDK for SAP ABAP provides an interface to the services offered by AWS in the ABAP language
2. Cloud Platforms & Services
SAP BTP (Business Technology Platform)
- Acronym: SAP Business Technology Platform
- Category: Cloud Platform
- Purpose: Integrated platform-as-a-service that combines database and data management, analytics, integration, and extension capabilities. Serves as the foundation for developing and integrating business applications in the cloud.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: N/A (current strategic platform)
- Key Use Cases: Application development, system integration, data analytics, and extending SAP and non-SAP applications.
IAM Governance Application Development Ai Embedded Integration Data & Analytics
3. Integration & Connectivity Tools
SLT (SAP Landscape Replication Server)
- Acronym: SAP Landscape Transformation Replication Server
- Category: Integration & Connectivity Tools
- Purpose: Real-time data replication tool that enables data transfer between different SAP systems and from SAP to non-SAP systems. Supports both real-time and scheduled data replication scenarios.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: SAP Data Intelligence for some use cases
- Key Use Cases: System migrations, data replication to HANA, real-time data synchronization, and landscape consolidation.
SAP Gateways
- Acronym: SAP Gateway (OData Gateway)
- Category: Integration & Connectivity Tools
- Purpose: Technology that enables the development of modern applications by providing RESTful APIs and OData services. Facilitates integration between SAP backend systems and various front-end applications including mobile and web applications.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: Enhanced API management in SAP BTP
- Key Use Cases: Mobile application development, web application integration, API development, and system-to-system integration.
Web Dispatcher
- Acronym: SAP Web Dispatcher
- Category: Integration & Connectivity Tools
- Purpose: Software load balancer and reverse proxy that distributes HTTP/HTTPS requests across multiple SAP application servers. Provides load balancing, SSL termination, and security features for web-based SAP applications.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: Cloud-native load balancing solutions for cloud deployments
- Key Use Cases: Load balancing web requests, SSL termination, security gateway, and high availability for web applications.
4. Database Systems
SAP R/3 Traditional Databases
- Acronym: Various - Oracle Database, IBM DB2, Microsoft SQL Server, SAP MaxDB
- Category: Database Systems
- Purpose: Traditional row-oriented, disk-based relational database management systems that served as the backend for SAP R/3 and ECC systems. Provided reliable transactional processing with separate systems required for analytical workloads.
- Lifecycle Stage: Legacy/Maintenance (still supported for existing R/3/ECC installations)
- Replacement Technology: SAP HANA (for S/4HANA migrations)
- Key Use Cases: Legacy SAP R/3 and ECC systems, traditional ERP operations, established production environments requiring proven stability, and organizations with existing database expertise and infrastructure investments.
HANA Database
- Acronym: SAP High-Performance Analytic Appliance
- Category: Database System
- Purpose: In-memory, column-oriented, relational database management system that processes both transactional and analytical workloads in real-time. Enables lightning-fast data processing and real-time analytics.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: N/A (current strategic database)
- Key Use Cases: S/4HANA backend, real-time analytics, data warehousing, and high-performance transactional processing.
| ERP Function | Traditional DB | HANA DB | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Order Processing | 3-5 seconds | < 1 second | 3-5x faster |
| Financial Reporting | Hours/Days | Minutes | 10-100x faster |
| Inventory Lookup | 2-10 seconds | < 1 second | 2-10x faster |
| MRP Run | 30-180 minutes | 5-30 minutes | 6-36x faster |
| Period Close | 2-5 days | 4-8 hours | 6-15x faster |
| Analytics Queries | Minutes/Hours | Seconds | 60-3600x faster |
Read Further
5. Development & Programming Tools
ABAP Programming Language
- Acronym: Advanced Business Application Programming
- Category: Development & Programming Tools
- Server/Backend Application
- Purpose: SAP's proprietary programming language designed for developing business applications on SAP platforms. Provides extensive capabilities for data processing, user interface development, and system integration.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active (evolved for cloud)
- Replacement Technology: ABAP continues to evolve; cloud development also supports other languages
- Key Use Cases: Custom business logic development, reports, interfaces, conversions, enhancements, and workflow development.
SAP UI5
- Acronym: SAP User Interface 5 (also known as OpenUI5 for the open-source version)
- Category: Development & Programming Tools
- Client/Frontend Application
- Purpose: JavaScript-based framework for developing responsive, cross-platform web applications with native-like user experience. Provides a rich set of UI controls, data binding capabilities, and follows modern web development patterns.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: N/A (current strategic UI framework, though evolving toward SAP Fiori Elements and other modern approaches)
- Key Use Cases: Custom web application development, Fiori app development, modernizing SAP GUI transactions, mobile-responsive applications, and extending SAP applications with modern user interfaces.
6. Application Platforms & Frameworks
SAP NetWeaver
- Acronym: SAP NetWeaver Application Server
- Category: Application Platforms & Frameworks
- Purpose: Technology platform that provides the runtime environment for SAP applications and serves as an integration platform for both SAP and non-SAP applications. Includes application server, integration capabilities, and development tools.
- Lifecycle Stage: Legacy/Maintenance
- Replacement Technology: SAP BTP for new developments
- Key Use Cases: Running traditional SAP ERP systems, custom ABAP developments, and system integrations.
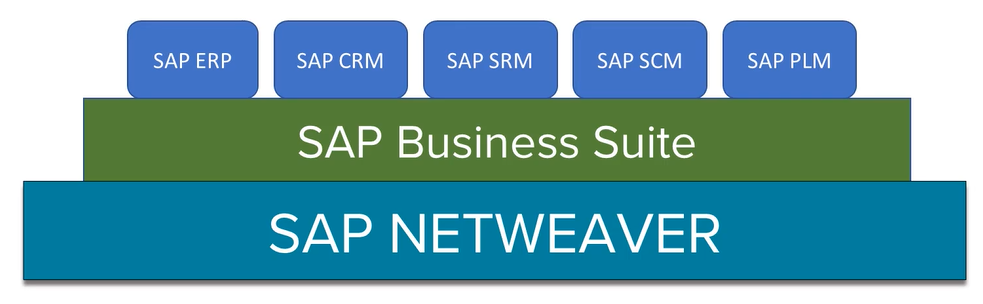
SAP R/3 (pronounce: R three)
- Acronym: SAP R/3 (Real-time system, 3-tier architecture)
- Category: Application Platforms & Frameworks
- Purpose: Traditional enterprise resource planning system built on a three-tier client-server architecture, providing integrated business applications for finance, logistics, and human resources. Served as SAP's flagship ERP solution for over two decades, establishing the foundation for modern enterprise software.
- Lifecycle Stage: End of Life (mainstream maintenance ended 2015)
- Replacement Technology: SAP S/4HANA (current strategic platform)
- Key Use Cases: Legacy ERP operations, traditional batch processing, established business process automation, and foundational enterprise resource planning for organizations maintaining older SAP installations.
S/4HANA (pronounce: S four)
- Acronym: SAP S/4HANA (SAP Business Suite 4 SAP HANA)
- Category: Application Platforms & Frameworks
- Purpose: Next-generation business suite built on SAP HANA platform, offering real-time processing, simplified data models, and modern user experience. Represents SAP's digital core for intelligent enterprises.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: N/A (current strategic platform)
- Key Use Cases: Digital transformation, real-time business processes, integrated planning, and intelligent automation.
7. Administration & Management Tools
SAP ASCS (ABAP messaging layer)
- Acronym: ABAP Central Services (ASCS)
- Category: Administration & Management Tools
- Purpose: Critical infrastructure component that hosts the message server and enqueue server for SAP systems. Provides load balancing, inter-server communication, and data consistency management through centralized lock table administration. Essential for system reliability and high availability architecture.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active (core component of modern SAP NetWeaver architecture)
- Replacement Technology: Continues to evolve with SAP NetWeaver enhancements and cloud-native architectures
- Key Use Cases: Load balancing user requests, managing inter-application server communication, ensuring data integrity through lock management, and enabling high-availability SAP system configurations.
SAP BASIS
- Acronym: Business Application Software Integrated Solution (BASIS)
- Category: Administration & Management Tools
- Purpose: Technical foundation and administration layer for SAP systems that manages system installation, configuration, performance monitoring, user administration, and system maintenance. Provides the underlying technical infrastructure for all SAP applications.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active (evolved for HANA and cloud)
- Replacement Technology: Enhanced BASIS capabilities for S/4HANA and cloud administration tools
- Key Use Cases: System administration, performance tuning, user management, transport management, and system monitoring.
Solution Manager
- Acronym: SAP Solution Manager
- Category: Administration & Management Tools
- Purpose: Centralized platform for implementing, operating, monitoring, and maintaining SAP solutions. Provides tools for project management, testing, change management, and system monitoring across the entire SAP landscape.
- Lifecycle Stage: Legacy
- Replacement Technology: SAP Cloud ALM (Application Lifecycle Management)
- Key Use Cases: Implementation project management, system monitoring, change and transport management, and solution documentation.
8. Business Application Modules
MM (Materials Management)
- Acronym: Materials Management
- Category: Business Application Modules
- Purpose: Manages procurement processes, inventory management, and material master data. Handles purchasing, goods receipt, invoice verification, and inventory valuation within the supply chain.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active (evolved in S/4HANA)
- Replacement Technology: Enhanced MM functionality in S/4HANA
- Key Use Cases: Procurement operations, inventory control, vendor management, and supply chain optimization.
SD (Sales & Distribution)
- Acronym: Sales and Distribution
- Category: Business Application Modules
- Purpose: Manages the complete order-to-cash process including sales order processing, delivery, billing, and customer master data. Integrates with other modules to provide comprehensive sales management.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active (evolved in S/4HANA)
- Replacement Technology: Enhanced SD functionality in S/4HANA
- Key Use Cases: Sales order management, pricing, delivery processing, billing, and revenue recognition.
PM (Plant Maintenance)
- Acronym: Plant Maintenance
- Category: Business Application Modules
- Purpose: Manages maintenance activities for technical systems and equipment including preventive maintenance, breakdown maintenance, and maintenance planning. Ensures optimal equipment performance and availability.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active (evolved in S/4HANA)
- Replacement Technology: Enhanced PM functionality in S/4HANA with predictive maintenance capabilities
- Key Use Cases: Equipment maintenance, work order management, maintenance scheduling, and asset lifecycle management.
CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
- Acronym: Customer Relationship Management
- Category: Business Application Modules
- Purpose: Manages customer interactions, sales processes, marketing campaigns, and service operations. Provides 360-degree view of customer relationships and enables personalized customer experiences.
- Lifecycle Stage: Legacy (on-premise) / Active (cloud)
- Replacement Technology: SAP Sales Cloud, SAP Service Cloud, SAP Marketing Cloud
- Key Use Cases: Customer data management, sales force automation, marketing campaign management, and customer service.
GRC (Governance, Risk & Compliance)
- Acronym: Governance, Risk and Compliance
- Category: Business Application Modules
- Purpose: Helps organizations manage corporate governance, assess and mitigate risks, and ensure compliance with regulations and internal policies. Provides frameworks for risk management and compliance monitoring.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: Enhanced GRC capabilities in cloud solutions
- Key Use Cases: Risk assessment, compliance monitoring, audit management, and regulatory reporting.
SRM (Supplier Relationship Management)
- Acronym: Supplier Relationship Management
- Category: Business Application Modules
- Purpose: Manages supplier relationships, procurement processes, and vendor performance. Facilitates collaboration with suppliers and optimizes procurement operations through strategic sourcing and supplier evaluation.
- Lifecycle Stage: Legacy
- Replacement Technology: SAP Ariba, enhanced procurement capabilities in S/4HANA
- Key Use Cases: Supplier qualification, strategic sourcing, contract management, and supplier performance monitoring.
9. Analytics & Reporting Tools
BW (Business Warehouse)
- Acronym: SAP Business Warehouse
- Category: Analytics & Reporting Tools
- Purpose: Enterprise data warehouse solution that provides data modeling, extraction, transformation, and loading capabilities. Serves as central repository for business intelligence and analytical reporting.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active (BW/4HANA version)
- Replacement Technology: BW/4HANA for new implementations
- Key Use Cases: Data warehousing, business intelligence, analytical reporting, and data integration from multiple sources.
SAC (SAP Analytics Cloud)
- Acronym: SAP Analytics Cloud
- Category: Analytics & Reporting Tools
- Purpose: Cloud-based analytics platform that combines business intelligence, augmented analytics, and enterprise planning capabilities. Provides self-service analytics and collaborative planning in a single solution.
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Replacement Technology: N/A (current strategic analytics platform)
- Key Use Cases: Self-service analytics, financial planning, predictive analytics, and collaborative business planning.
10. User Interface & User Experience
SAP Fiori
- Purpose: Modern, intuitive, and responsive user interface design language for SAP applications
- Category: User Interface & User Experience
- Lifecycle Stage: Active
- Key Use Cases: Providing consistent, role-based user experiences across SAP applications, mobile-friendly interfaces, and simplified user interactions
- Fiori applications typically run on:
- SAP Gateway
- SAP UI5 framework
- Integrate with various SAP backend systems like S/4HANA
Integration & Relationship Matrix
SAP Modules and S/4HANA Integration
The traditional SAP modules (MM, SD, PM, etc.) have been reimagined and tightly integrated within S/4HANA. In the legacy ERP environment, these modules operated as separate functional areas with defined integration points. S/4HANA breaks down these silos through the Universal Journal, which provides a single source of truth for all financial and operational data.
For example, when a sales order is created in SD within S/4HANA, it immediately triggers real-time availability checks in MM (inventory), updates financial postings through the Universal Journal, and can initiate production planning in PP if needed. This level of integration was not possible in traditional ERP systems due to their batch-oriented architecture.
SAP BASIS and System Components
SAP BASIS serves as the technical foundation that enables all other SAP components to function. It manages the application servers where ABAP programs run, handles database connectivity (including HANA DB), manages user sessions, and provides the technical infrastructure for business modules like MM, SD, and PM.
In S/4HANA environments, BASIS administrators must understand both traditional BASIS concepts and HANA-specific administration. This includes HANA studio management, in-memory computing optimization, and real-time replication scenarios.
BTP and On-Premise Integration
SAP BTP serves as the bridge between on-premise SAP systems and cloud applications. Through various integration services, BTP can extend existing ERP functionality, provide new user experiences, and integrate with third-party systems.
For instance, a company running on-premise S/4HANA can use BTP to develop mobile applications that access real-time data, create analytical dashboards using SAP Analytics Cloud, or integrate with external systems through BTP's integration capabilities.
HANA Database Across SAP Products
HANA DB is not just the database for S/4HANA; it serves as the foundation for multiple SAP products. BW/4HANA uses HANA for analytical processing, SAP Analytics Cloud connects to HANA for real-time analytics, and various other SAP applications leverage HANA's in-memory capabilities.
The relationship is particularly important in landscapes where multiple SAP products share the same HANA database instance, requiring careful resource management and optimization.
Integration Patterns
Modern SAP landscapes employ various integration patterns. API-first approaches using SAP Gateway enable real-time integrations, while traditional RFC and IDoc mechanisms continue to support batch integrations. SLT provides real-time data replication capabilities, and BTP's integration services offer cloud-native integration patterns.
Lifecycle & Migration Paths
Legacy to Modern Transitions
The SAP ecosystem is undergoing significant transformation from traditional on-premise systems to cloud-native solutions. Key migration paths include:
Traditional ERP systems are being migrated to S/4HANA through various approaches including system conversion, new implementation, and selective data transition. Each approach has different implications for existing customizations, integrations, and business processes.
SAP NetWeaver-based custom developments are being modernized to run on SAP BTP, taking advantage of cloud-native capabilities and modern development paradigms. This transition often involves re-architecting applications to leverage microservices, APIs, and cloud-native databases.
Legacy CRM and SRM systems are being replaced by cloud solutions like SAP Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, and Ariba. These transitions typically involve data migration, process reengineering, and integration with remaining on-premise systems.
Technology Sunset and Evolution
Several SAP technologies are in maintenance mode or approaching end of life. SAP NetWeaver Application Server continues to be supported but new developments are directed toward BTP. Traditional Business Warehouse is being replaced by BW/4HANA for new implementations. Solution Manager is being superseded by SAP Cloud ALM for application lifecycle management.
Understanding these lifecycle stages is crucial for career planning and technology investment decisions. Professionals should focus on gaining expertise in current and future technologies while maintaining knowledge of legacy systems for migration projects.
Interview Preparation Quick Reference
Most In-Demand Skills
S/4HANA expertise is highly sought after, particularly experience with finance (FICO), supply chain (MM/PP), and sales (SD) modules. HANA database administration and optimization skills are valuable across all SAP roles. SAP BTP development capabilities, especially integration services and extension development, are increasingly important.
ABAP development remains relevant, but modern ABAP for S/4HANA and cloud development is preferred over traditional ABAP. BASIS administration skills are always in demand, with particular value placed on S/4HANA BASIS and cloud administration expertise.
Foundation vs. Specialized Technologies
Foundation technologies include SAP BASIS, ABAP programming, and core module knowledge (MM, SD, FICO). These skills provide the baseline for most SAP careers. Specialized technologies include HANA administration, BTP development, SAC analytics, and specific integration tools like SLT or SAP Gateway.
Career progression typically starts with foundation skills and gradually incorporates specialized technologies based on role requirements and market demands. Technical roles often emphasize BASIS and development skills, while functional roles focus on business modules and process optimization.
Common Interview Topics
Technical interviews often cover system architecture questions about how different SAP components interact, particularly the relationship between business modules and underlying technical infrastructure. Functional interviews focus on business process knowledge and how SAP modules support specific industry scenarios.
Scenario-based questions are common, such as explaining how a purchase order flows through MM, SD, and financial modules, or describing the technical architecture of an S/4HANA system. Integration questions frequently address how different systems communicate and share data.
Market Relevance Priorities
Current market priorities emphasize cloud-first approaches, real-time analytics, and integrated business processes. S/4HANA transformation projects dominate the market, creating demand for migration expertise. Digital transformation initiatives drive need for BTP and analytics capabilities.
Industry-specific knowledge combined with SAP expertise is particularly valuable, especially in manufacturing, retail, and utilities sectors. Sustainability and ESG reporting capabilities are emerging as important differentiators.
Glossary
ABAP: Advanced Business Application Programming - SAP's proprietary programming language for developing business applications.
API: Application Programming Interface - A set of protocols and tools for building software applications that allow different systems to communicate.
BASIS: The technical foundation layer that provides runtime, database, and operating system independence for SAP applications.
BTP: Business Technology Platform - SAP's integrated platform-as-a-service for developing and integrating business applications.
HANA: High-Performance Analytic Appliance - SAP's in-memory database platform that processes both transactional and analytical data in real-time.
IDoc: Intermediate Document - SAP's standard data format for electronic data interchange between systems.
OData: Open Data Protocol - A web protocol for querying and updating data that enables REST-based data services.
RFC: Remote Function Call - SAP's protocol for communication between different systems or between different modules within the same system.
Transport: The process of moving configuration changes, custom developments, and other objects between SAP systems in a landscape.
Universal Journal: S/4HANA's unified data model that combines financial and management accounting data in a single table structure.