AWS Storage Services Overview
AWS offers a comprehensive suite of storage services designed to meet diverse application requirements, from high-performance computing to long-term archival.
Block Storage
Block storage provides persistent, low-latency block-level storage volumes that attach to EC2 instances like physical hard drives. Block storage volumes can be
- encrypted
- backed up via snapshots
- modified without disrupting the instance.
Amazon EC2 Instance Store: An unmanaged non-persistent, high-performance block storage directly attached to EC2 instances for temporary data.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS): A managed service that provides persistent block storage volumes for EC2 instances. EBS volumes persist independently of EC2 instances and can be attached, detached, and reattached as needed.

Object Storage
Object storage is a data storage architecture that manages data as objects in a flat address space. It offers:
- Unlimited scalability.
- Object storage provides enhanced metadata.
- Efficient data management, search, and analytics.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3): A fully managed scalable object storage service for storing and retrieving any amount of data from anywhere. S3 offers multiple storage classes to optimize costs based on access patterns and provides industry-leading durability of 99.999999999% (11 9's).
Object storage is ideal for web applications, content distribution, backup and archiving, data analytics, and static website hosting. Unlike block storage, objects are accessed via REST APIs rather than being mounted as drives.
File Storage
AWS file storage services provide shared file systems accessible over networks, so multiple users and applications can access the same data simultaneously. They offer scalability and flexibility so you can expand storage capacity as needs grow without managing physical infrastructure.
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS): A fully managed, scalable NFS file system for use with AWS Cloud services and on-premises resources. EFS automatically scales storage capacity up or down as files are added or removed, and supports concurrent access from multiple EC2 instances.
Amazon FSx: A fully managed file storage service for popular file systems like Windows, Lustre, and NetApp ONTAP. FSx provides high-performance file systems optimized for specific workloads such as high-performance computing, media processing, and enterprise applications.

Additional Storage Services
These services don't fit cleanly into the traditional storage categories but provide important hybrid and disaster recovery capabilities.
AWS Storage Gateway: A fully managed, hybrid-cloud storage service that provides on-premises access to virtually unlimited cloud storage. It connects on-premises environments to AWS storage services through a virtual machine or hardware appliance.
AWS Elastic Disaster Recovery: A fully managed service that streamlines the recovery of your physical, virtual, and cloud-based servers into AWS. It provides continuous data replication and enables rapid recovery in case of system failures or disasters.
AWS Shared Responsibility Model for Storage
The AWS shared responsibility model groups storage services into three categories based on the ownership of administrative tasks: fully managed, managed, and unmanaged services.
Fully Managed Services: For fully managed storage services. Examples include Amazon S3 and Amazon EFS.
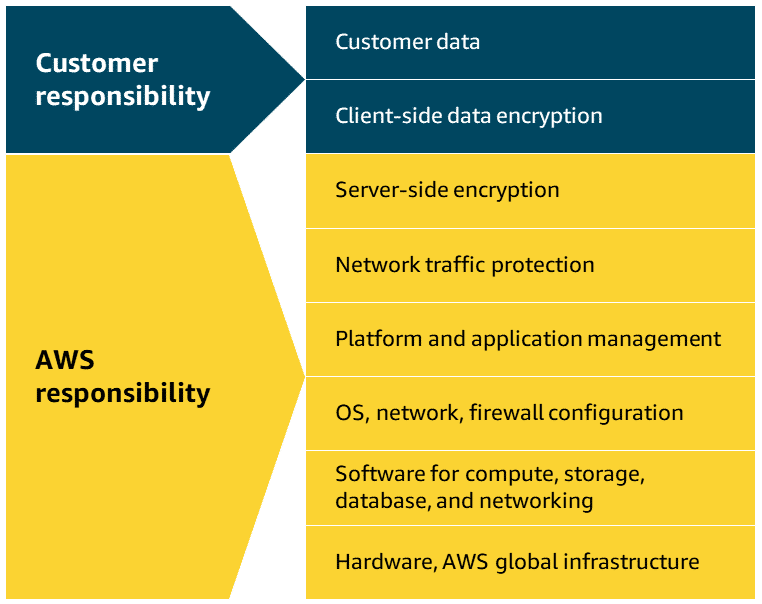
Managed Services: For managed storage services, AWS manages the underlying storage infrastructure, hardware redundancy, and volume replication. Customers are responsible for data backup strategies, encryption configuration, volume performance optimization, and capacity planning. Amazon EBS falls into this category.
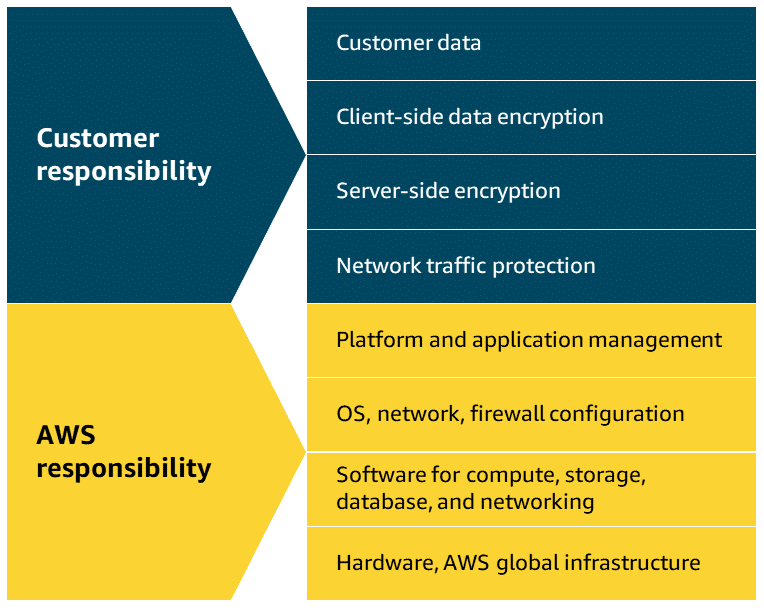
Unmanaged Services: For unmanaged storage services, customers take full responsibility for data management, backup and recovery, encryption, performance optimization, and durability. AWS only maintains the underlying physical hardware and network infrastructure. EC2 instance store is an example of unmanaged storage.
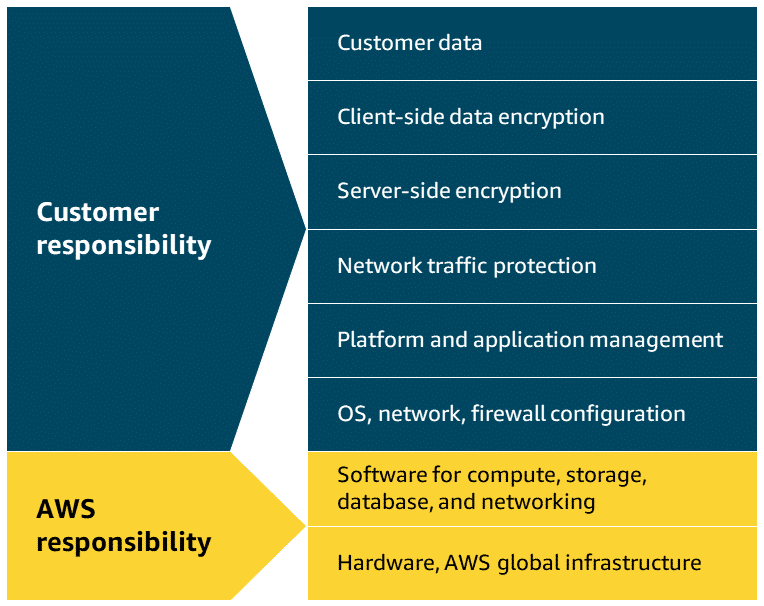
Understanding these responsibility boundaries helps ensure proper security, compliance, and operational practices when implementing AWS storage solutions.