Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Amazon EBS provides persistent block-level storage volumes for EC2 instances, acting like external hard drives that retain data even when instances are stopped or terminated.
Key EBS Characteristics
- Persistent Storage: Data survives instance stops, starts, and termination unlike instance store
- Independent Lifecycle: EBS volumes exist independently of EC2 instances
- Attachable/Detachable: Volumes can be attached to different instances as needed
- Backup Capable: Supports point-in-time snapshots for data protection
- Scalable: Volume size and performance can be modified without downtime
Persistent vs Instance Store Comparison
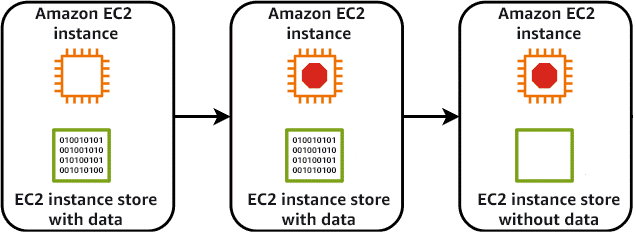
EC2 Instance Store:
- Temporary storage physically attached to host computer
- Data lost when instance stops or terminates
- No additional cost but no persistence
- High performance for temporary data
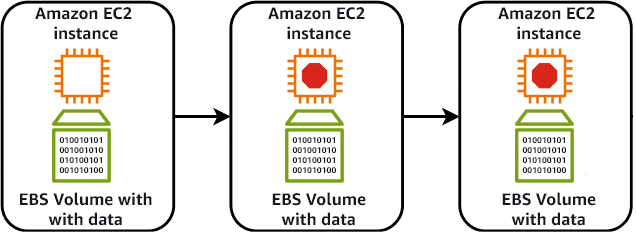
EBS Volumes:
- Network-attached persistent storage
- Data persists independently of instance state
- Additional cost but provides data durability
- Consistent performance with various volume types
Root vs Data Store Usage
Persistent Root Store: EBS can serve as the root volume containing the operating system, ensuring OS and configuration persistence across instance restarts.
Data Store: Additional EBS volumes can be attached for application data, databases, and file systems requiring long-term storage and backup capabilities.
Core Benefits
- Data Migration: Easy movement between Availability Zones using snapshots
- Instance Flexibility: Attach volumes to different instance types without data loss
- Disaster Recovery: Automated snapshots enable reliable backup and restore
- Cost Optimization: Modify volume types and sizes to match usage patterns
- Performance Tuning: Various volume types (gp3, io2, etc.) for different IOPS requirements
Benefits: EBS provides enterprise-grade persistent storage with snapshot backup, cross-AZ portability, and performance flexibility for mission-critical applications.
Use case: EBS is ideal for databases, file systems, enterprise applications, and any workload requiring data persistence beyond the EC2 instance lifecycle.