Understanding Amazon EC2 Instance Types
Amazon EC2 offers a vast selection of over 500 instance types, providing a wide range of choices in processors, storage, and networking. While this flexibility allows you to perfectly match an instance to a workload's needs, the sheer number of options can be overwhelming for new users trying to make an informed decision.
This guide breaks down how EC2 instances are categorized, named, and sized. By understanding this system, you can more easily navigate the options and select the most appropriate and cost-effective instance for your applications.
Core EC2 Concepts
Before diving into the specifics, it's important to understand the fundamental terminology.
- Instance: An EC2 instance is a virtual machine (VM) that runs in the AWS Cloud.
- Instance Type: This defines the virtual hardware configuration of your instance. It is the specific combination of CPU, memory, storage, and networking capacity.
- Instance Family: Instance types are grouped into families based on their optimization for specific use cases (e.g., compute-intensive, memory-intensive).
- vCPU (Virtual Central Processing Unit): This is the primary measure of an instance's processing power. For most instances, one vCPU corresponds to a single hardware thread of a physical CPU core.
The Five Core Instance Families
AWS categorizes instances into five distinct families, each optimized for different types of workloads.
General Purpose
- Description: These instances provide a balance of compute, memory, and networking resources. They are ideal for a wide variety of diverse workloads.
- Use Cases: Web servers, code repositories, microservices, development and testing environments, and small to medium databases.
- Family Letters:
T,M,A
Compute Optimized
- Description: These instances are designed for compute-bound applications that benefit from high-performance processors. They offer the best price-performance for compute-intensive tasks.
- Use Cases: High-performance computing (HPC), batch processing, media transcoding, scientific modeling, dedicated gaming servers, and ad serving engines.
- Family Letter:
C
Memory Optimized
- Description: These instances are designed to deliver fast performance for workloads that process large datasets in memory.
- Use Cases: In-memory databases (like Redis or Memcached), real-time big data analytics (like Apache Spark or Hadoop), and other high-performance databases.
- Family Letters:
R,X,Z
Storage Optimized
- Description: These instances are designed for workloads that require high, sequential read and write access to very large datasets on local storage. They are optimized to deliver tens of thousands of low-latency, random IOPS.
- Use Cases: NoSQL databases (Cassandra, ScyllaDB), data warehousing, Elasticsearch, and analytics workloads.
- Family Letters:
I,D,H
Accelerated Computing
- Description: These instances use hardware accelerators, or co-processors, to perform functions more efficiently than is possible in software running on CPUs.
- Use Cases: Machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), high-performance computing (HPC), graphics-intensive applications, and data pattern matching.
- Family Letters:
P,G,F,Trn,Inf
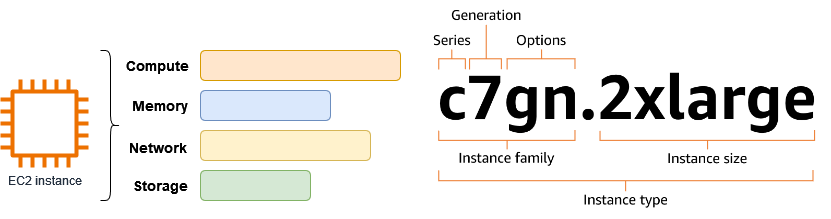
Decoding EC2 Instance Names
EC2 instance names follow a structured format that reveals key characteristics about the instance at a glance. The name is a combination of family, generation, additional capabilities, and size.
Let's take the instance name c6gn.xlarge as an example.
c: The instance family (Compute Optimized).6: The instance generation (6th generation). Newer generations typically offer better price-performance.g: An additional capability modifier (AWS Graviton processor).n: Another additional capability modifier (Network optimization).xlarge: The instance size within the family.
Additional Capability Modifiers
The letters between the generation number and the size indicate special features. Here are some of the most common modifiers:
| Modifier | Meaning | Description |
|---|---|---|
a | AMD Processors | The instance uses AMD EPYC processors. |
g | AWS Graviton Processors | The instance uses AWS-designed, Arm-based Graviton processors. |
i | Intel Processors | The instance uses Intel Xeon processors. |
d | Instance Store Volumes | The instance includes a local, high-performance NVMe SSD instance store. |
n | Network Optimization | The instance supports higher network bandwidth (up to 100 Gbps). |
b | Block Storage Optimization | The instance offers optimized performance for Amazon EBS. |
e | Extra Storage or Memory | The instance has a higher memory-to-vCPU ratio or more storage. |
z | High Frequency | The instance features a high-frequency processor (sustained all-core turbo). |
Understanding Instance Sizing
Within each family, instances are offered in various sizes (e.g., nano, micro, small, medium, large, xlarge, 2xlarge, up to 32xlarge) to allow you to scale resources for your workload.
The way resources scale up with size depends on the instance family's optimization. For General Purpose T instances, the vCPU count stays the same for smaller sizes, while memory doubles with each step up.
| Instance Family | Instance Size | vCPU | Memory (GiB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Purpose | t4g.nano | 2 | 0.5 |
| General Purpose | t4g.micro | 2 | 1 |
| General Purpose | t4g.small | 2 | 2 |
| General Purpose | t4g.medium | 2 | 4 |
| General Purpose | t4g.large | 2 | 8 |
GiB vs. GB: AWS prices and measures memory in gibibytes (GiB), where 1 GiB = 1024³ bytes. This is distinct from a gigabyte (GB), which is 1000³ bytes. While the difference is small at lower scales, it becomes significant for large memory configurations.
In contrast, Compute Optimized and Memory Optimized families scale both vCPU and memory, with a focus on their primary resource.
| Instance Family | Instance Size | vCPU | Memory (GiB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compute Optimized | c5.xlarge | 4 | 8 |
| Compute Optimized | c5.2xlarge | 8 | 16 |
| Compute Optimized | c5.4xlarge | 16 | 32 |
| Memory Optimized | r6g.xlarge | 4 | 32 |
| Memory Optimized | r6g.2xlarge | 8 | 64 |
| Memory Optimized | r6g.4xlarge | 16 | 128 |
By understanding this logical system of families, naming conventions, and sizing, you can efficiently narrow down the vast catalog of EC2 instances to find the perfect fit for your workload's technical and budgetary requirements.