Elastic Load Balancing (ELB)
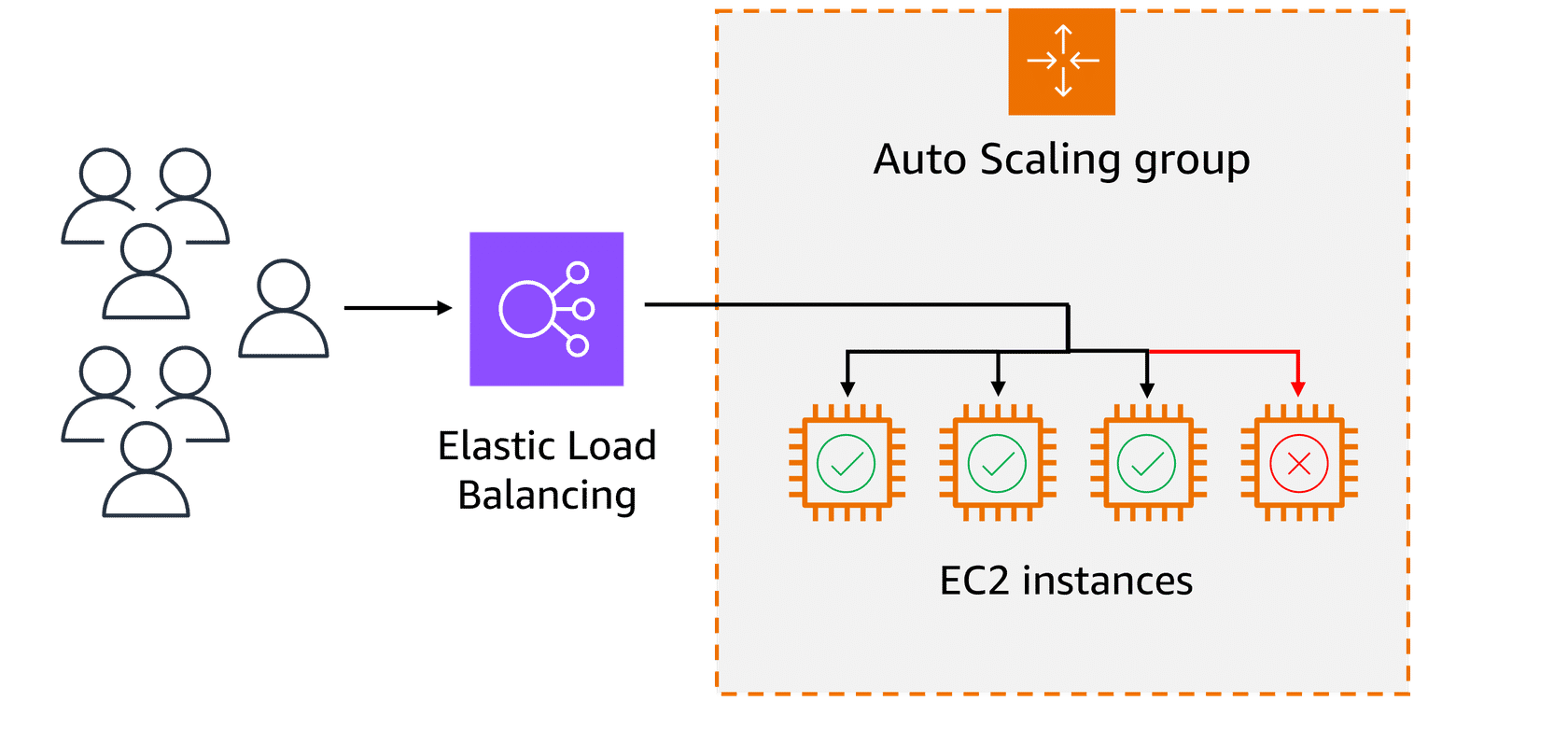
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple resources, such as EC2 instances, to optimize performance and reliability.
ELB and Amazon EC2
Although ELB and Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling are distinct services, they work in tandem to enhance application performance and ensure high availability. Together, they enable applications running on Amazon EC2 to scale effectively while maintaining consistent performance.
ELB benefits
-
Efficient traffic distribution: ELB evenly distributes traffic across EC2 instances, preventing overload on any single instance and optimizing resource utilization.
-
Automatic scaling: ELB scales with traffic and automatically adjusts to changes in demand for a seamless operation as backend instances are added or removed.
-
Simplified management: ELB decouples front-end and backend tiers and reduces manual synchronization. It also handles maintenance, updates, and failover to ease operational overhead.
Routing methods
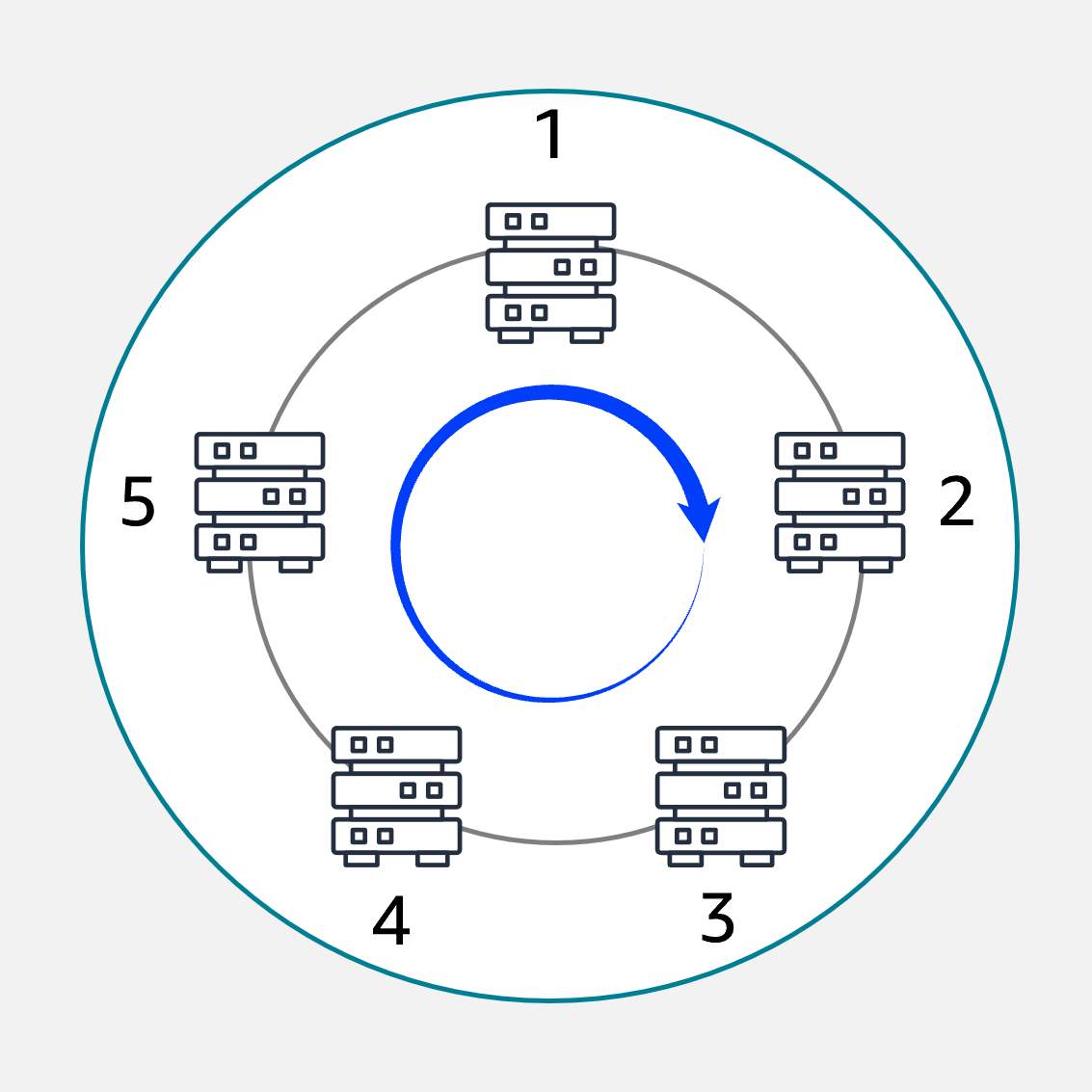
Round Robin
Distributes traffic evenly across all available servers in a cyclic manner.
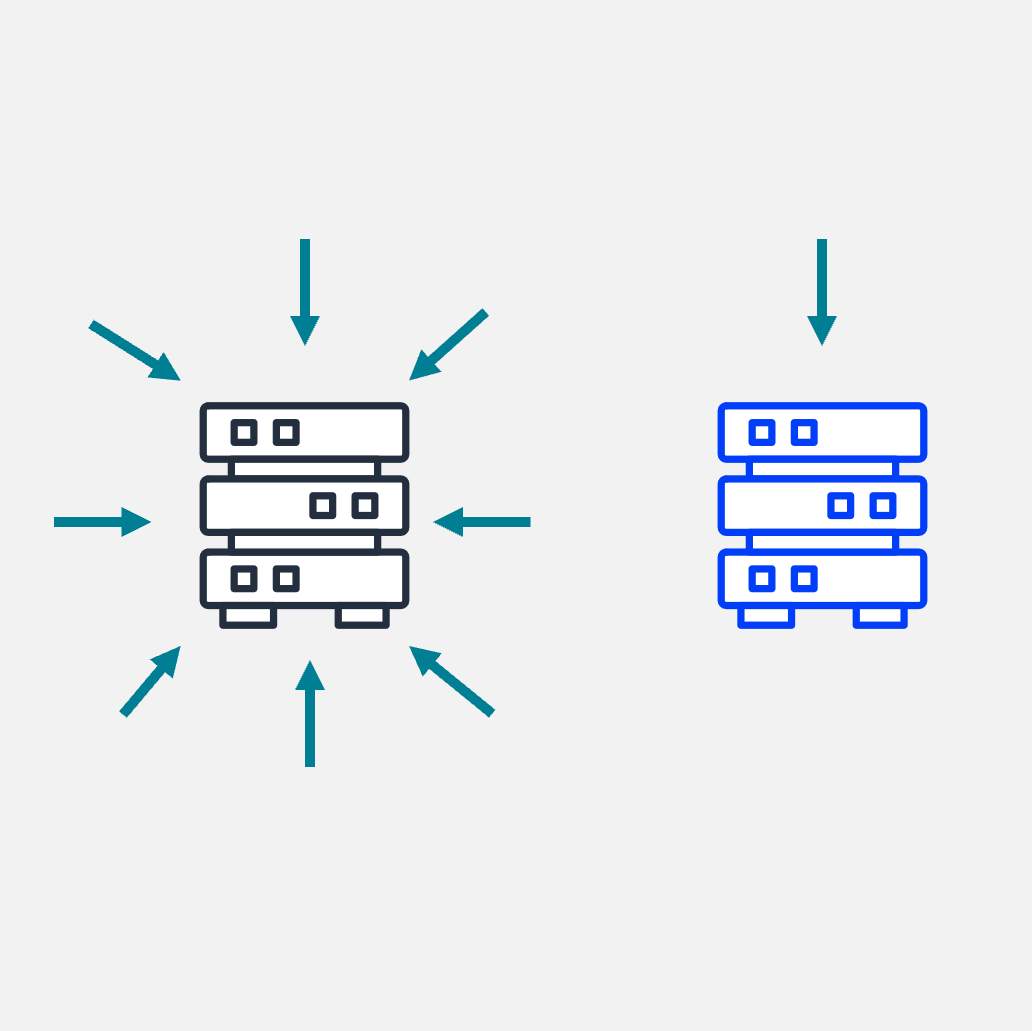
Least Connections
Routes traffic to the server with the fewest active connections, maintaining a balanced load.
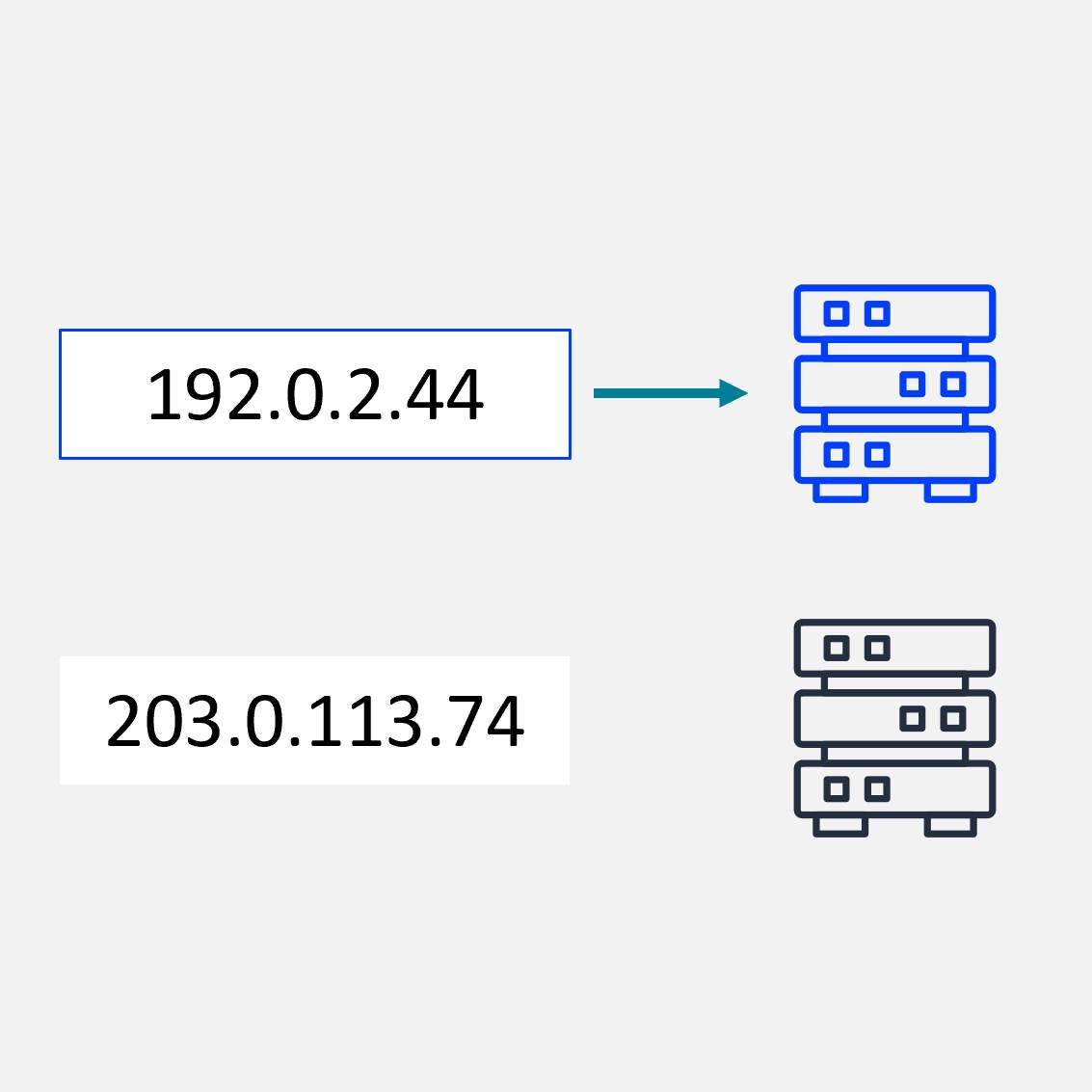
IP Hash
Uses the client’s IP address to consistently route traffic to the same server.
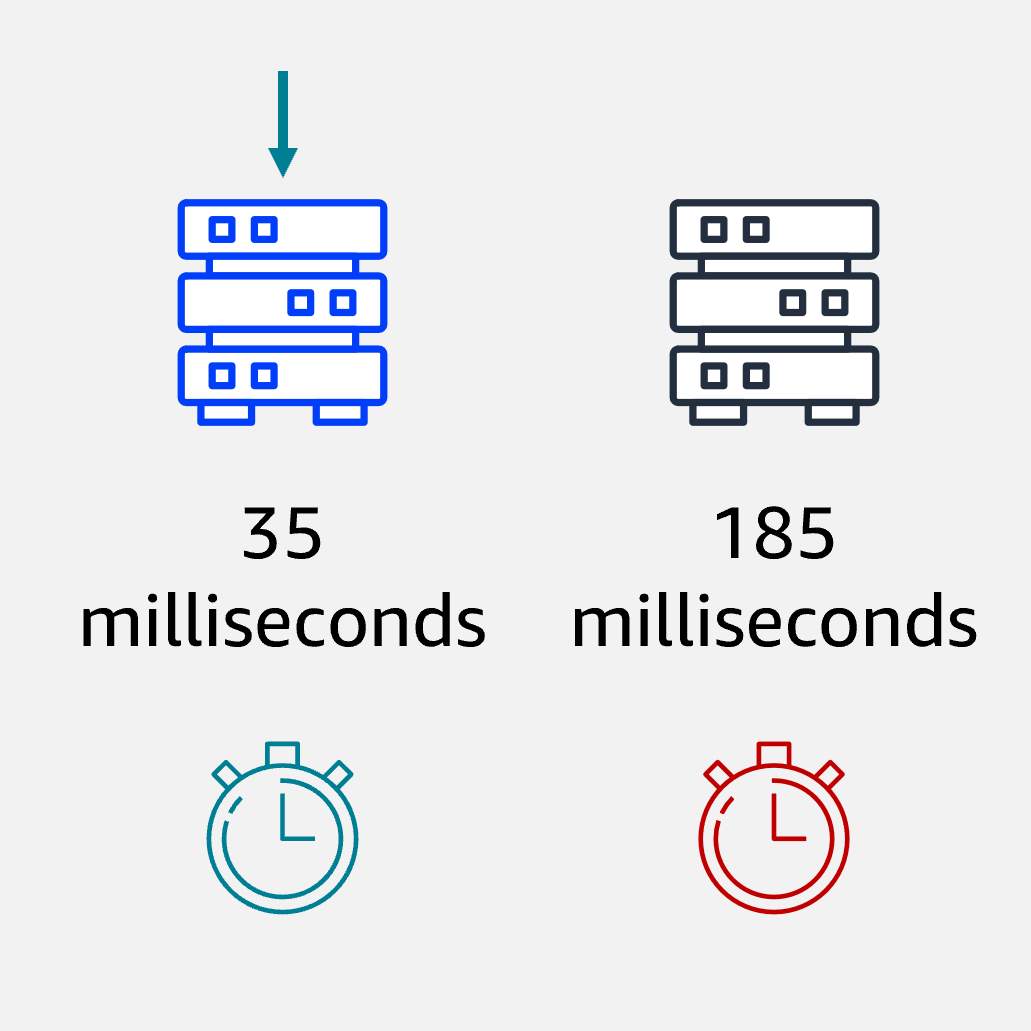
Least Response Time
Directs traffic to the server with the fastest response time, minimizing latency.
Elastic Load Balancing
For better understand how Elastic Load Balancing works in cloud computing. In the healthcare industry that provide online systems or patient portals, website traffic can vary greatly throughout the day.
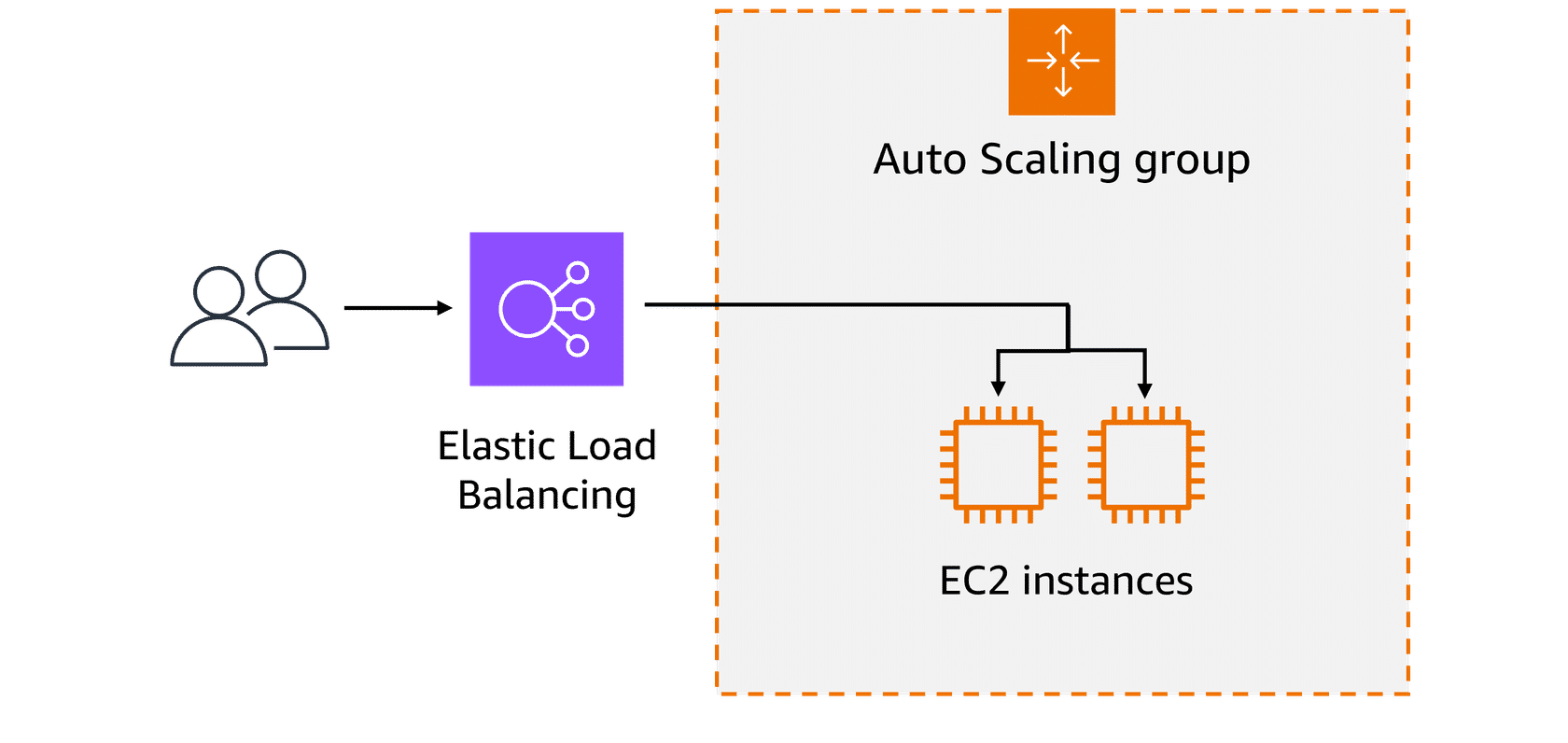
Low-demand period:
At the beginning of the day, only a few patients are accessing the system to book appointments or view medical records. The existing web servers are sufficient to handle the low traffic. This matches the demand, with no need for additional resources at this point.
High-demand period:
As the day progresses, especially during peak hours, such as early mornings or just before the weekend, more patients access the portal to book appointments, view test results, or contact medical professionals. To handle this surge in demand, the healthcare system automatically scales up the number of servers to help ensure that the system remains responsive and available for all users.
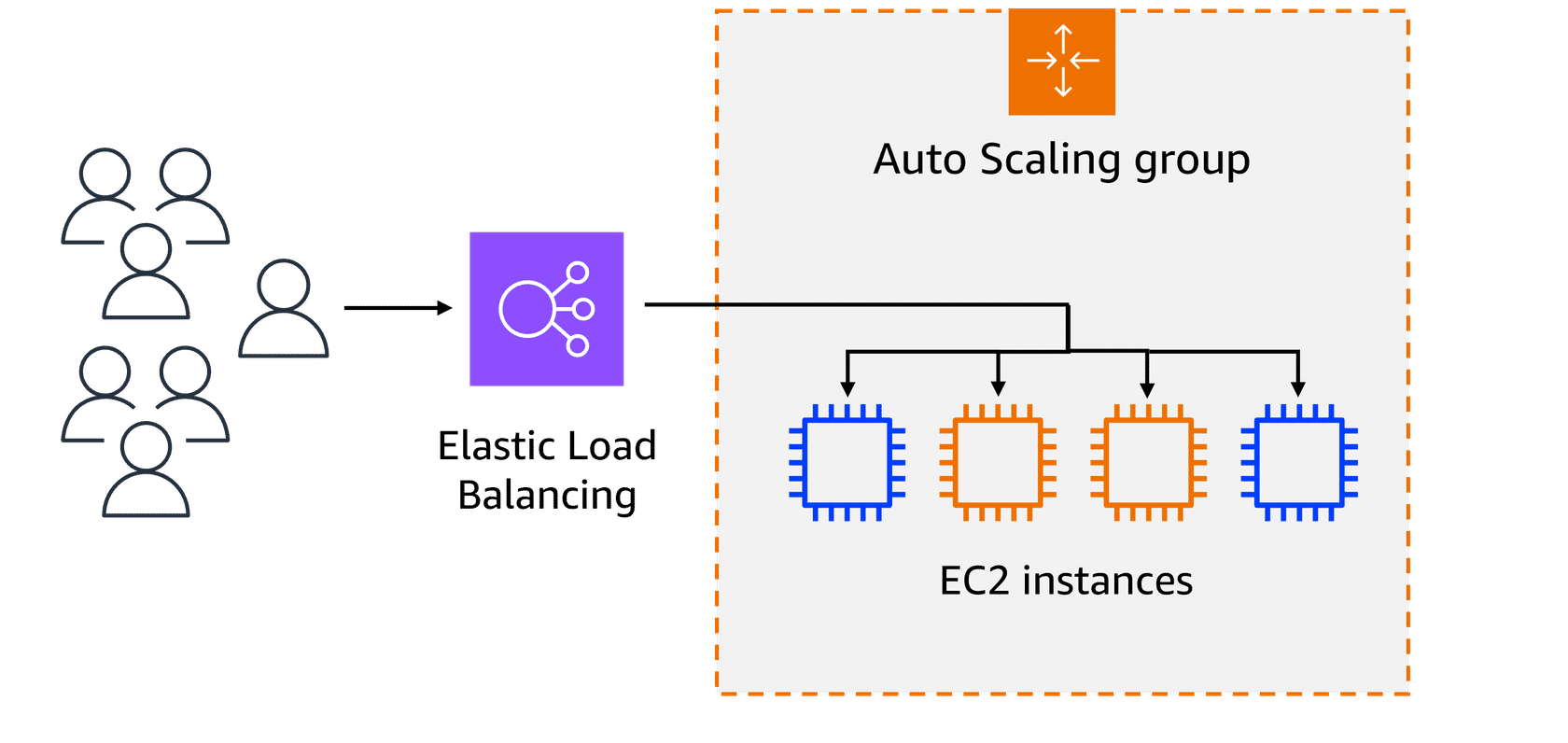
Load Balncing:
A load balancer directs the incoming traffic to different web servers based on their current load. For instance, if one server starts receiving too many requests, the load balancer will route new requests to a less busy server. This makes sure that no single server becomes overwhelmed. The traffic is evenly distributed across available EC2 instances.